
No New Fossil Fuel Projects: The norm we need
A social-moral norm against new fossil fuel projects has strong potential to contribute to achieving global climate goals
A collaboration between University College London and IISD shows that existing fossil fuel capacity is sufficient to meet the 1.5°C-aligned energy demand. The article recommends a "No New Fossil Fuels" norm, which would prevent new fossil fuel exploration and extraction projects and the construction of new fossil fuel power plants. This new fossil fuel development ban would be easier politically, economically, and legally than closing operational projects early.
-
Peer-reviewed science shows there is no room for new oil and gas fields or gas- and coal-fired power plants in a 1.5°C world.
-
Enabling new fossil fuel development is incompatible with climate leadership.
-
Preventing new development is a sensible first step to implement the transition away from fossil fuels.
Experts from IISD and the University College London have co-authored an article in the academic journal Science, entitled "No New Fossil Fuel Projects: The Norm We Need." It is the first peer-reviewed article to show that there is no room for new fossil fuel projects under a 1.5°C global warming limit. The article argues that a feasible first step to phasing out fossil fuels is to stop licensing new oil and gas fields and building coal and gas-fired power plants.
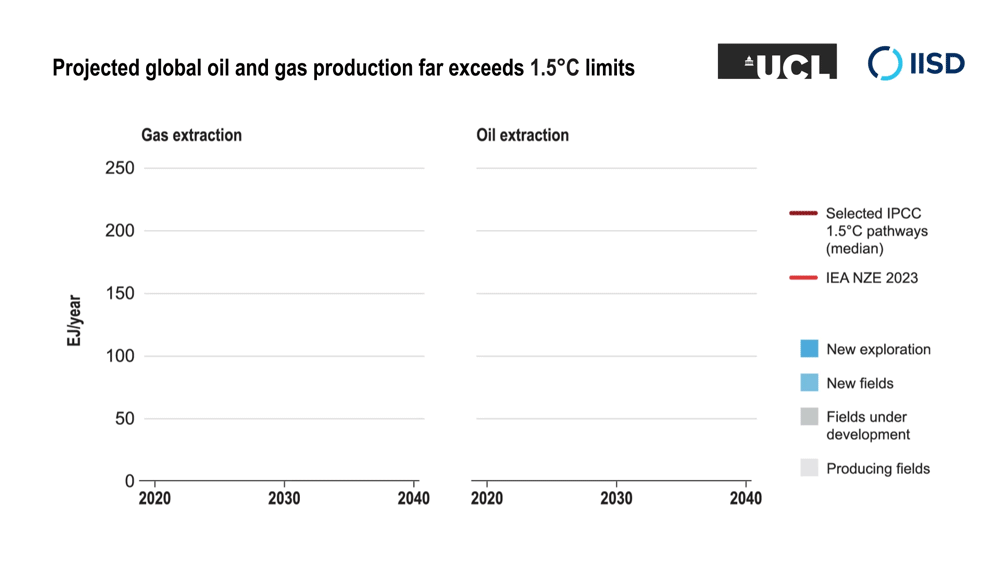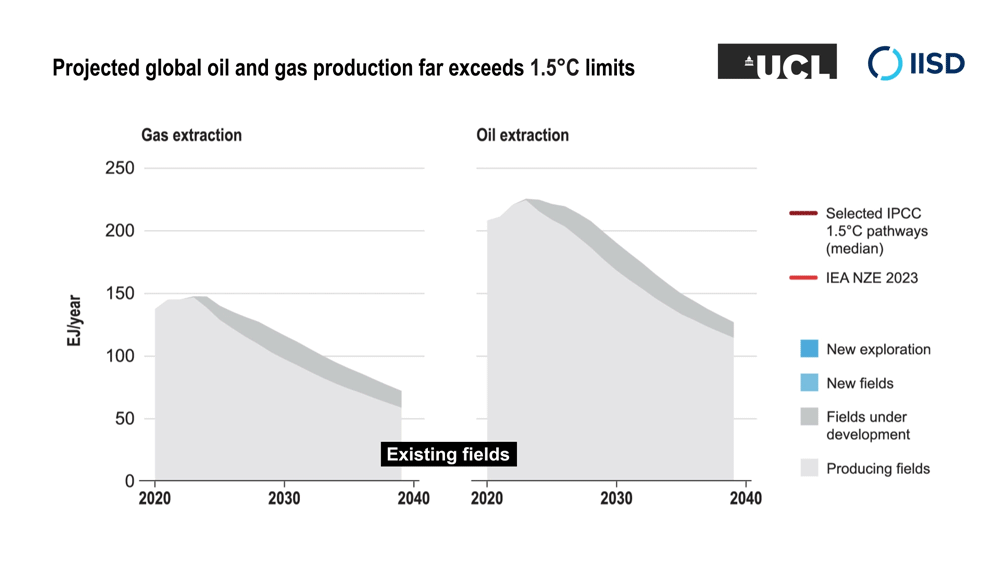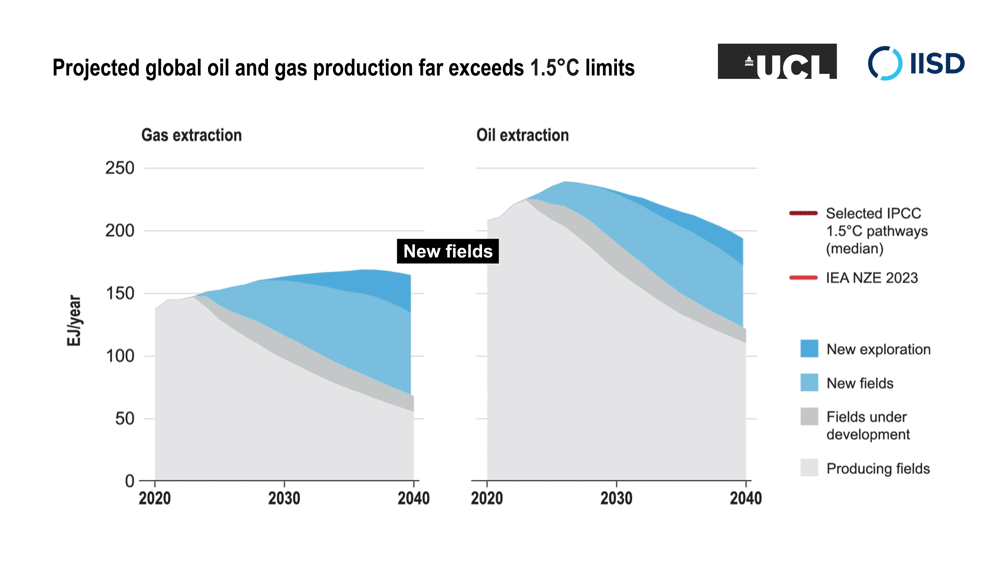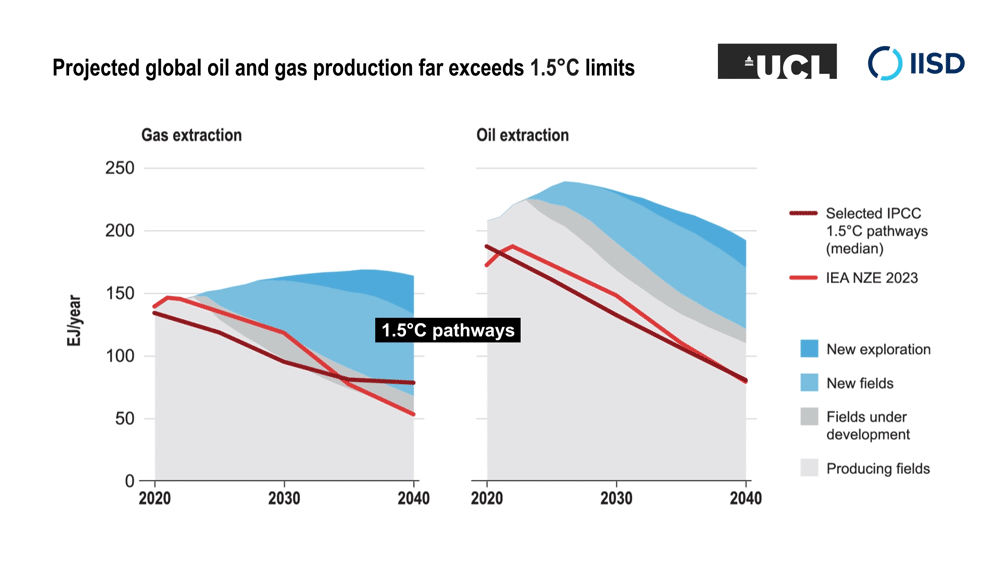
The researchers analyzed the projected future global demand for oil and gas production, and for coal- and gas-fired power generation, under a range of modelled scenarios that limit climate change to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. It shows that existing fossil fuel capacity is sufficient to meet energy demand under these scenarios while the planet transitions to clean and renewable energy—and that new fossil fuel projects are not necessary.
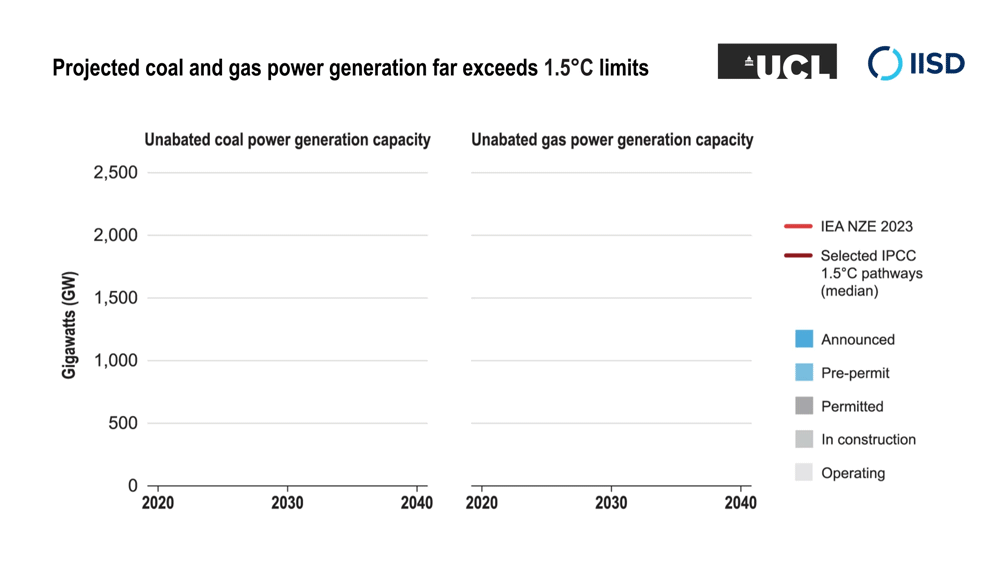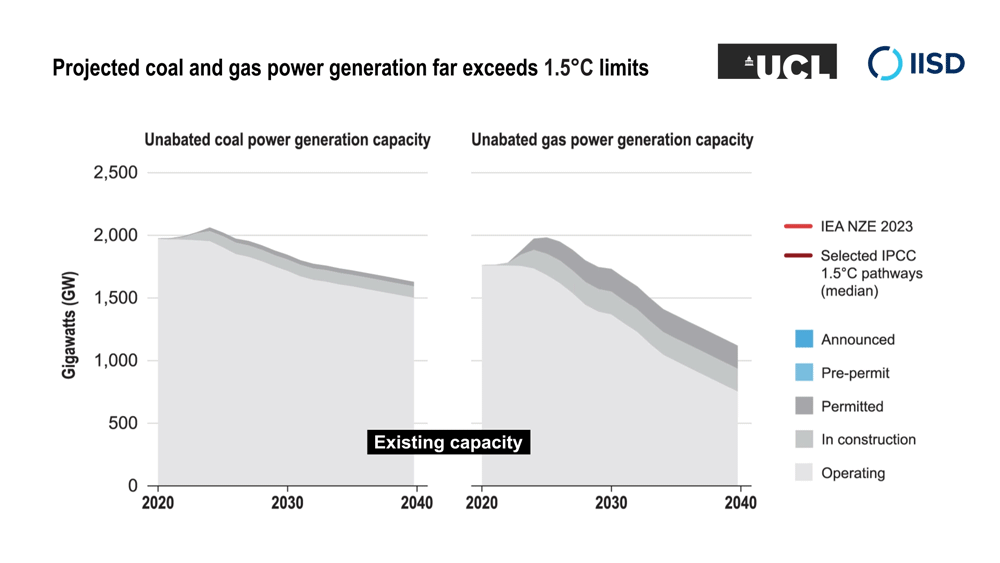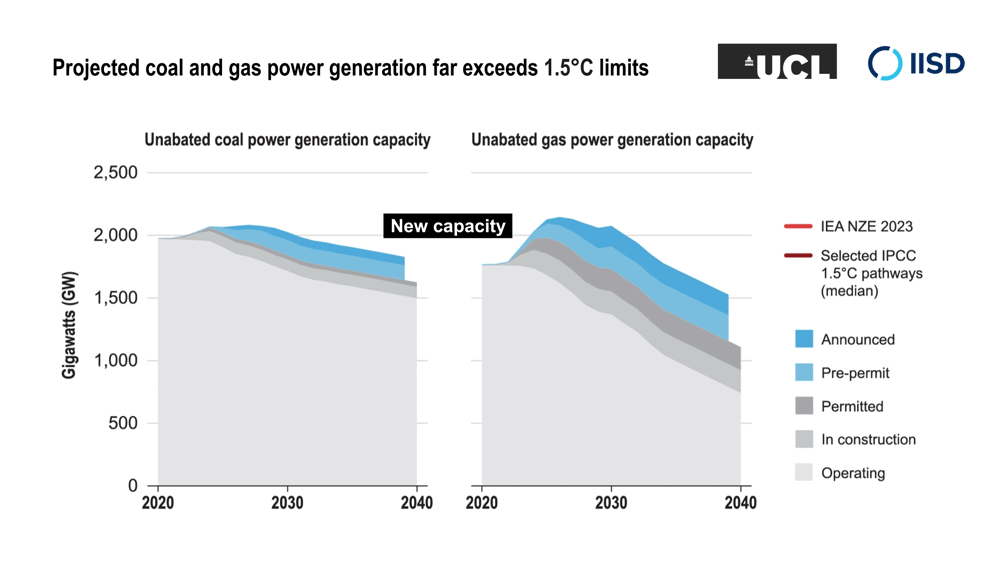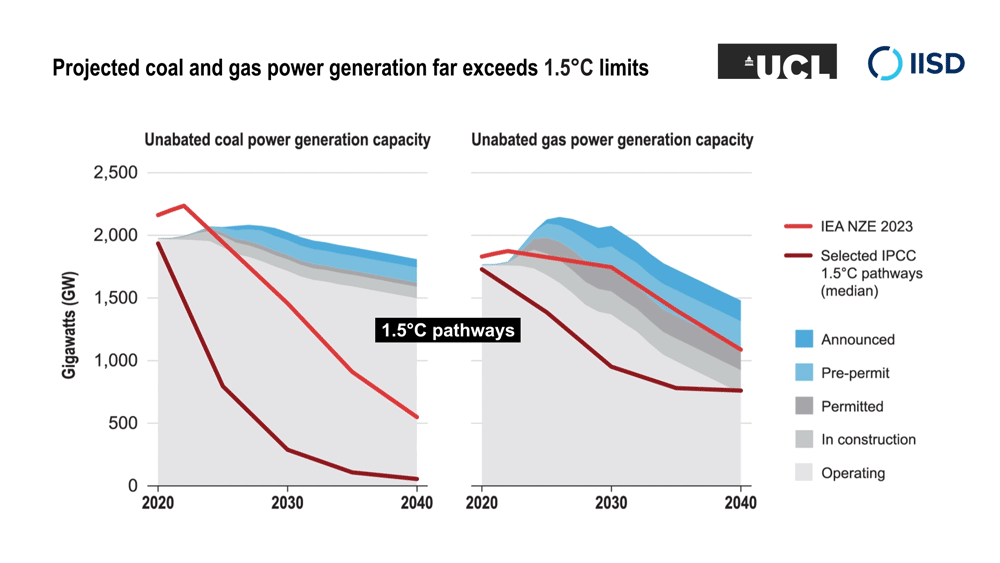
The research extends work by the International Energy Agency that found in a 2021 report (updated in 2023) that no new fossil fuel extraction projects are needed in the transition to net-zero emissions by 2050. The research team’s new work expands on this by analyzing a broad range of scenarios compiled for the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s Sixth Assessment Report that limit climate change to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Their analysis found that, in addition to not needing new fossil fuel extraction, no new coal- and gas-fired power generation was needed.
Participating experts
You might also be interested in
March 2025 | Carbon Minefields Oil and Gas Exploration Monitor
Last month, a total of 22 oil and gas exploration licences were awarded across six countries, with an estimated volume of discovered resources of 45.4 million barrels of oil and 10.4 billion cubic feet of gas.
February 2025 | Carbon Minefields Oil and Gas Exploration Monitor
In January 2025, 77 oil and gas exploration licences were awarded in seven different countries, with Norway leading in terms of embodied emissions.
January 2025 | Carbon Minefields Oil and Gas Exploration Monitor
Last month, a total of 78 oil and gas exploration licences were awarded in two countries. The United States had the largest volume of embodied emissions in the licences it awarded.
December 2024 | Carbon Minefields Oil and Gas Exploration Monitor
In November 2024, 23 oil and gas exploration licences were awarded across five countries, with Russia granting the licences that account for the largest portion of embodied emissions.